Introduction to heat energy
Heat is a form of energy and it is very crucial to all living things.
Properties of heat
Other sources:
Home electrical applicants:
The water in our wet clothes evaporates to form water vapour when heat is gained from the sun.

Heat transfer through conduction
- It cannot be seen but it can be felt
- Always flows from a hotter object to a colder object
- Can change the state of matter
e.g.- Solid change to liquid
- liquid change to gas
- Can change the temperature of an object

|
Sun is the main source of heat. It is also a natural source of heat. Other natural sources of heat are volcanoes and geysers.
|
- toaster
- kettle
- light blub
- oven
- computer
- television
- charcoal
- oil
- gas
- wood

|

|

|

|
|||
| Ice melting is a change of stage from solid to liquid. (Heat gain) |
Water boiling to steam is a change of stage from liquid to gas. (Heat gain) |
Water vapour contact with cool surface (condensation) is a change of stage from gas to liquid (Heat loss) |
Water turn to ice is known as freezing It is a change of stage from liquid to solid. (Heat loss) |

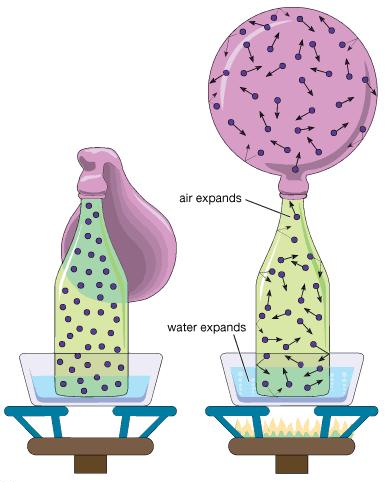 |
Heat gain can cause expansioon in matter.
For example, the inflating of a bolloon attached to an empty bottle. When heated, the air inside bottle expand causing the ballon to be inflated. |
- Conduction is the transfer of heat energy through matter.
- Conduction require a medium such as solid, liquid or gas.
- Materials that allow heat to flow through them quickly are considered as good conductors of heat e.g. metal while materials that allow heat to flow very slow are considered poor conductors of heat or insulators.
